BI PLASTICS
Environmental
Technology
THE TYPES OF BIOPLASTICS
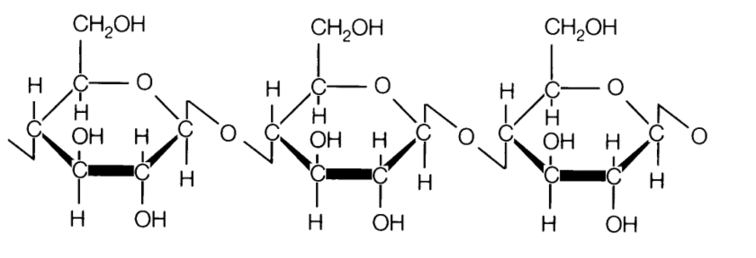
Starch is a carbohydrate used as a main component in plastics. Starch-based bioplastics are often blended with biodegradable polyesters making them compostable. Films that are composed of starch and blended with thermoplastic polyesters are often used in the manufacturing of plastic products.
STARCH
Also known as Polylactic Acid, this is a biodegradable thermoplastic aliphatic polyester derived from renewable resources. Studies show that in 2010, PLA reached the second highest consumption volume of any other bioplastic. It is most commonly used for degradable packaging purposes as it can be easily developed in facilities for petrochemical-based plastics.
PLA


PA 11
Polymide 11 or Nylon 11 is a polymide and bioplastic derived from castor beans and natural oils. This source is a good chemical resistance, a low water absorbing nylon, and has the ability to accept high loading of filters. PA 11 is primarily used in high-performing applications and it is much more efficient and cheaper compared to other metals and rubber.
BIO-PE
Bio-polyethylene is a polyethylene from ethanol which converts to ethylene after a dehydration process at temperatures between 300 and 600°C. It's physical properties makes it useful for conversion into plastic products making it versatile and environmental friendly. Bio-pe secretes around 2,150 tons of CO2 which is absorbed by the sugarcane, limiting and reducing the production of harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
CELLULOSE
Cellulose is a substance that makes up the majority of a plant's cell walls making it the world's most abundant organic compound. Cellulose is also described by scientists to be a complex carbohydrate. Celluloid and cellophane, just some of the first industrial polymers, both came from the production of cellulose. After cellulose is mixed together with camphor, a crystalline and terpene ketone from the camphor tree, it will produce the plastic known as celluloid which was primarily used for films.





- potato
- corn
- wheat
- rice
Comes from:
Used in:
- cosmetics
- shopping bags
- antibiotics
- water-soluble chips
- hygiene products


Used in:
Comes from:
- packaging
- furniture
- insulators
- hygiene products
- sugarcane
- tapioca
- potato
Used in:
Comes from:
-castor beans
- automotive fuel lines
- oil and gas flexible pipes
- sports shoes
Used in:
Comes from:
- sugarcane
- wheat grain
- sugar beet
- automotive fuel lines
- oil and gas flexible pipes
- sports shoes
Comes from:
Used in:
- cotton
- wood
- hemp
- flax
- plastics
- furniture
- toys
- paper
- films